Enhance Your Athletic Performance through Effective Protein Strategies
Discover How Protein Supports Muscle Recovery and Repair for Athletes

Protein is an essential component for athletes striving to optimise their recovery and muscle repair processes. This crucial macronutrient plays a significant role in healing muscle tissues that endure damage during intensive workouts, ultimately promoting faster recovery and muscle growth. Insufficient protein intake can lead to prolonged recovery times, heightened muscle soreness, and decreased performance capabilities. The advantages of integrating sufficient protein into an athlete’s dietary regimen are profound, including:
- Enhanced muscle repair: Protein is vital for the synthesis of new muscle tissue, which is critical for efficient recovery.
- Reduced muscle soreness: Adequate protein consumption can significantly lessen the intensity and duration of post-exercise discomfort.
- Improved muscle growth: Protein is instrumental in facilitating hypertrophy, which is essential for athletes looking to increase strength and muscle mass.
- Accelerated recovery: Consuming protein after workouts expedites recovery, allowing athletes to train more effectively.
- Maintenance of lean muscle mass: Protein aids in preventing muscle loss, especially during calorie deficits or intensive training phases.
- Strengthened immune function: Sufficient protein intake bolsters the immune system, crucial for athletes subjected to high levels of physical stress.
Grasping the role of protein in muscle repair enables athletes to refine their recovery techniques. The timing and quantity of protein consumed can greatly influence the effectiveness of muscle recovery following strenuous activities. Athletes engaged in high-intensity training or sports that impose significant muscle damage must prioritise their protein intake as a fundamental element of their overall nutritional strategy.
How Much Protein Do Athletes Require for Optimal Performance?
The protein requirements of athletes are highly individualised and can vary significantly. Factors such as the specific sport, intensity of training, and body weight are pivotal in determining personal protein needs. For instance, endurance athletes typically require around 1.2 to 1.4 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, while strength athletes generally need between 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram to effectively stimulate muscle growth and promote recovery.
Recognising these protein needs is essential for achieving peak athletic performance. Athletes participating in rigorous training should evaluate their daily protein consumption and make necessary modifications based on their training demands. A well-structured diet that corresponds with training intensity and objectives can significantly enhance athletic performance while reducing the risk of injury.
Identifying the Best Sources of High-Quality Protein for Athletes
Acquiring high-quality protein from a diverse array of sources is vital for athletes. Both animal and plant-based sources are available, each offering unique nutritional benefits. Animal-based options such as lean meats, fish, dairy, and eggs provide complete proteins that contain all essential amino acids required for muscle repair and growth.
Conversely, plant-based options like legumes, quinoa, tofu, and nuts also present valuable protein, albeit they may lack certain essential amino acids. However, by combining various plant sources, athletes can achieve a complete amino acid profile.
Notable high-quality protein sources include:
- Chicken and turkey: These lean meats are excellent sources of protein with low fat content.
- Fish: Varieties like salmon and tuna deliver protein along with heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids.
- Eggs: A versatile source of complete protein that can be prepared in numerous ways.
- Dairy products: Foods like yogurt and cottage cheese offer outstanding protein and calcium sources.
- Legumes: Beans and lentils provide a high-fibre, plant-based protein option.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds and chia seeds offer protein and beneficial fats for heart health.
Incorporating a varied selection of these sources into daily meals can assist athletes in effectively meeting their protein needs. It is crucial for athletes to explore both animal and plant-based proteins to construct a balanced diet that supports their training and overall well-being.
Optimising Protein Intake Timing for Maximum Recovery and Growth

The timing of protein intake is a crucial factor for maximising its benefits. Consuming protein at strategic intervals throughout the day—particularly after workouts—can considerably enhance muscle recovery and growth. Research indicates that the body is especially receptive to protein intake within a window of approximately 30 minutes to two hours post-exercise, commonly referred to as the “anabolic window.”
Ideal timings for protein consumption include:
- Post-workout: Consuming protein immediately after training promotes recovery and muscle repair.
- Pre-workout: Eating protein beforehand can supply amino acids during exercise.
- Before bedtime: A slow-digesting protein source can assist in muscle repair overnight.
- Spread throughout the day: Distributing protein intake evenly across meals enhances muscle synthesis.
By concentrating on these optimal times for protein consumption, athletes can improve their recovery and performance potential. Whether through whole foods or supplements, strategic protein timing is essential for anyone aspiring to achieve their athletic goals.
When and Why Should Athletes Consider Protein Supplementation?
Protein supplementation can serve as a valuable resource for athletes who struggle to meet their protein needs through dietary sources alone. This is particularly relevant for individuals with high training demands or dietary restrictions that limit protein intake. Supplements provide a practical and effective means to boost protein consumption while supporting recovery and muscle growth.
There are various forms of protein supplements available, such as whey, casein, and plant-based options, each with distinct advantages. Whey protein, known for its rapid absorption, is often preferred for post-workout recovery, while casein protein digests slowly, making it beneficial for overnight recovery.
Advantages of protein supplementation include:
- Convenience: Easily integrates into busy schedules, especially for athletes on the move.
- Targeted nutrition: Allows for precise protein intake to meet specific dietary goals.
- Enhanced recovery: Facilitates quicker recovery times post-exercise, enabling more frequent training sessions.
- Variety: Available in a range of flavours and formats, making it easier to find a suitable option.
For athletes, understanding when and why to utilise protein supplements can lead to improved performance and recovery. While whole foods should remain the cornerstone of nutrition, supplements can effectively bridge dietary gaps when necessary.
Expert Insights on Daily Protein Utilisation Among Athletes
Real-World Case Studies of Effective Protein Application
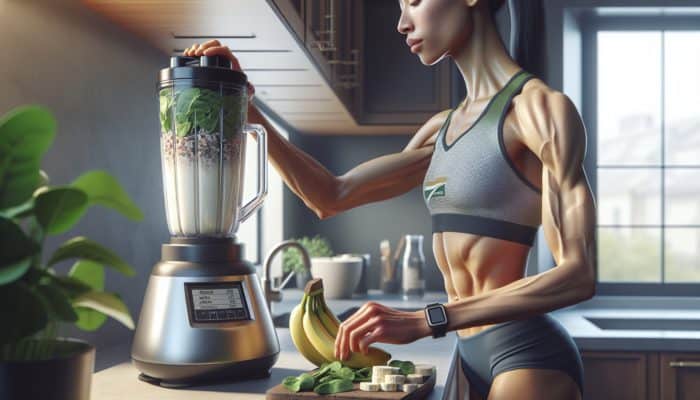

Real-world case studies provide valuable insights into how athletes effectively incorporate protein into their daily routines. Consider the example of an elite marathon runner who prioritises protein in her post-workout recovery shake. She blends whey protein with a banana and spinach, ensuring she replenishes her body with essential nutrients after extensive training sessions. By consuming protein shortly after her workouts, she accelerates recovery and prepares her body for upcoming sessions.
Another case involves a professional rugby player who starts his day with a protein-rich breakfast. His morning meal comprises eggs, avocado on whole-grain toast, and Greek yogurt, creating a balanced dish that supports his demanding training sessions. This combination not only provides protein but also delivers essential fats and carbohydrates, all vital for peak performance.
Practical strategies for athletes to optimise their protein consumption include:
- Meal planning around training: Ensure that protein-rich foods are readily available for post-workout recovery.
- Utilise snacks strategically: Incorporate high-protein snacks like nuts or protein bars to meet daily intake goals.
- Experiment with supplements: Try various protein powders to find the right fit for personal taste and performance needs.
- Track protein intake: Use apps or journals to monitor protein consumption and adjust as needed.
These examples highlight the different methods athletes can effectively prioritise protein in their diets. By tailoring their protein sources and timing to their unique needs and routines, athletes can enhance their performance and overall health.
What Are the Optimal Times to Consume Protein for Best Results?
Strategically timing protein intake can dramatically enhance its effectiveness. Athletes should concentrate on specific times throughout the day to maximise the advantages of protein consumption. Notably, the post-workout period is crucial for muscle recovery and growth. However, there are additional key times when protein should be consumed to support overall performance.
Optimal protein consumption times include:
- Immediately post-workout: To initiate muscle recovery and replenish essential amino acids.
- Breakfast: Starting the day with protein supports muscle maintenance and energy levels.
- Before bedtime: Consuming a slow-digesting protein before sleep aids in overnight recovery.
- Pre-exercise: Eating protein prior to workouts can provide energy and prevent muscle breakdown.
By timing protein intake effectively, athletes can significantly enhance recovery and performance outcomes. This approach ensures they remain at the peak of their abilities and maintain a competitive advantage.
How Can Athletes Ensure They Are Consuming High-Quality Protein Sources?
Ensuring access to high-quality protein sources is crucial for athletes aiming to meet their nutritional needs efficiently and safely. High-quality protein sources contain all essential amino acids, which are vital for optimal muscle repair and growth. Athletes should focus on incorporating a blend of complete proteins from animal sources and complementary proteins from plant-based options.
When selecting protein sources, athletes should consider the following critical factors:
- Amino acid profile: Choose sources that deliver all essential amino acids.
- Digestibility: Opt for proteins that are easily digestible to maximise absorption.
- Nutritional density: Focus on sources that provide additional nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals.
- Source certification: Seek products certified for quality and purity, particularly supplements.
By concentrating on these factors, athletes can ensure they select high-quality protein options. This focus not only supports their performance goals but also contributes to overall health and wellness.
The Influential Role of Protein in Enhancing Athletic Performance
Understanding How Protein Boosts Athletic Performance
Protein plays a vital role in enhancing athletic performance. It contributes to improved muscle function, endurance, and overall physical capabilities. By supporting muscle repair and growth, protein aids athletes in recovering from strenuous training sessions and prepares their bodies for future performances.
Research indicates that adequate protein intake can lead to increased muscle mass and strength, which are directly related to improved performance across various sports. Furthermore, protein influences numerous bodily functions, including hormone production and immune response, both of which are essential for maintaining peak athletic performance.
Key mechanisms by which protein enhances performance include:
- Muscle repair: Facilitates the rebuilding of muscle tissue after challenging exercise.
- Muscle growth: Supports hypertrophy, essential for increasing strength and power.
- Energy provision: Can serve as an energy source during extended exercise or calorie restriction.
- Recovery enhancement: Reduces recovery time between workouts, allowing for more frequent training sessions.
Grasping the connection between protein and performance is crucial for athletes aiming to optimise their training regimens. By ensuring they consume adequate protein, athletes can enhance their physical capabilities and achieve superior overall performance outcomes.
How Protein Impacts Performance in Endurance Sports
Endurance athletes generally have unique protein requirements compared to strength athletes. While both groups need sufficient protein to aid in muscle recovery and growth, endurance athletes focus more on sustained energy and recovery. Research suggests that endurance athletes may benefit from slightly lower protein intakes, typically ranging from 1.2 to 1.4 grams per kilogram of body weight.
For endurance athletes, protein consumption helps preserve lean muscle mass during prolonged activities. Furthermore, it facilitates recovery, particularly after intense training sessions or extended competitions. Consuming protein alongside carbohydrates post-exercise can enhance glycogen replenishment, which is crucial for endurance performance.
Essential considerations for endurance athletes regarding protein intake include:
- Emphasise recovery: Prioritise protein intake immediately after extensive training sessions to support recovery.
- Combine with carbohydrates: Pairing protein with carbs optimises glycogen replenishment.
- Explore protein sources: Experiment with different protein sources to identify the best options for digestion during training.
- Maintain hydration: Proper hydration is essential for protein metabolism and recovery.
By understanding their distinct protein requirements, endurance athletes can tailor their diets to enhance performance and recovery. This focus on protein will enable them to maintain energy levels and improve overall endurance.
Protein Requirements for Strength and Power Athletes
Strength and power athletes necessitate higher protein intake to facilitate muscle growth and repair. For these athletes, protein is not merely a supplement; it is a crucial nutrient that directly affects their performance outcomes. Recommended protein intake for strength athletes typically ranges from 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Increased protein consumption promotes muscle hypertrophy, which is vital for building strength and power. Additionally, it aids in recovery, allowing athletes to engage in more frequent and intense training sessions without risking injury.
Key considerations for protein consumption in strength and power athletes include:
- Prioritise lean sources: Focus on high-quality protein sources low in fat.
- Utilise supplements strategically: Consider protein powders for convenience and post-workout recovery.
- Track intake: Monitor protein consumption to ensure it aligns with individual training demands.
- Incorporate variety: Use a mix of food sources to guarantee a comprehensive amino acid profile.
By emphasising protein intake, strength and power athletes can enhance their training and achieve superior results. This strategy allows them to optimise muscle growth, reduce recovery time, and maintain their competitive edge in their respective sports.
Research-Driven Insights on Protein Utilisation by Athletes
Examine Expert Analysis on Protein Research
Scientific research consistently reinforces the importance of protein in athletic diets. Numerous studies have demonstrated that increased protein intake correlates with improved muscle repair, enhanced recovery, and superior performance outcomes for athletes across various sports. Meta-analyses have established a strong link between protein consumption and muscle synthesis, underscoring the benefits of adequate protein intake in sports nutrition.
Research methodologies frequently employ controlled studies to evaluate the effects of protein on muscle recovery and performance. For instance, studies may compare groups of athletes consuming different levels of protein, assessing changes in muscle mass, strength, and recovery times. These findings consistently highlight the significance of prioritising protein in athletes’ diets to achieve optimal outcomes.
Key insights from protein research include:
- Increased muscle protein synthesis: Higher protein intake is directly linked to improved muscle recovery.
- Enhanced performance metrics: Athletes who consume adequate protein typically exhibit superior performance outcomes.
- Reduced injury risk: Sufficient protein intake may lower the likelihood of injuries associated with overtraining.
- Accelerated recovery: Protein consumption post-exercise significantly speeds up recovery times.
This evidence highlights the crucial role of protein in athletic performance. As athletes aim to optimise their training and enhance recovery, aligning their protein intake with scientific findings will yield better results.
What Are the Long-Term Advantages of Consistent Protein Intake?
Regular protein consumption offers numerous benefits for athletes over time. Sustained protein intake supports ongoing muscle health, decreases injury risk, and enhances overall athletic longevity. Over time, a strategic focus on protein can lead to improved performance and greater resilience against the physical demands of training.
Research indicates that athletes who maintain a high-protein diet can achieve improved body composition, characterised by increased lean muscle mass and a reduced body fat percentage. This balance is essential for optimising performance across various sports, enabling athletes to compete at higher levels with diminished fatigue.
Key long-term benefits of protein consumption include:
- Continuous muscle health: Persistent protein intake supports muscle repair and growth over time.
- Decreased injury risk: Adequate protein can diminish the chances of injuries due to muscle strain.
- Enhanced metabolic function: Protein consumption can elevate metabolic rates, aiding in body composition management.
- Quicker recovery times: Consistent protein intake can facilitate faster recovery between training sessions.
By recognising the long-term benefits of protein, athletes can make informed dietary choices that advance their athletic careers. This knowledge empowers them to sustain their health and improve their performance over time.
How Does Protein Impact Recovery Time Following Workouts?
Protein intake significantly shortens recovery time between workouts. After exercise, the body’s muscles undergo repair processes that necessitate an adequate supply of amino acids to rebuild. Consuming protein shortly after exercise can accelerate these processes, allowing athletes to recover more rapidly and resume training sooner.
Research has revealed that athletes who consume protein post-workout experience reduced muscle soreness and inflammation, resulting in shorter recovery periods. This not only facilitates more effective training sessions but also aids in preventing overtraining, which can lead to prolonged fatigue and injury.
Key ways in which protein affects recovery time include:
- Enhanced muscle repair: Protein intake provides the necessary building blocks for muscle recovery.
- Less soreness: Athletes report diminished muscle soreness when post-workout protein is consumed.
- Improved glycogen replenishment: Combining protein with carbohydrates aids in restoring energy levels.
- Facilitated adaptation: Adequate protein supports the body’s response to increased training loads.
By prioritising protein intake, athletes can effectively optimise their recovery strategies. This focus ensures they can train consistently and perform at their best in competitive situations.
Strategies for Effective Protein Supplementation
When Should Athletes Consider Integrating Protein Supplements?
Athletes may contemplate protein supplements when their dietary intake falls short. This situation can arise for various reasons, such as high training demands, dietary restrictions, or busy lifestyles that hinder the ability to consume sufficient whole food protein sources. Supplements offer a convenient means to augment protein intake, ensuring athletes meet their nutritional needs.
For instance, an athlete who struggles to meet their protein requirements through diet alone might opt for protein shakes or bars to bridge the gap. Additionally, during periods of intense training or competition, supplements can provide a practical solution for swift nourishment.
Key circumstances for protein supplementation include:
- High training volumes: When athletes engage in intense training, their protein needs increase.
- Dietary restrictions: Vegans or vegetarians may find it challenging to meet protein requirements through diet alone.
- Busy lifestyles: Supplements can conveniently supply protein on the go.
- Specific performance objectives: Athletes aiming for muscle gain may need additional protein support.
By recognising when to utilise protein supplements, athletes can ensure they meet their nutritional needs. This strategic approach to supplementation can enhance both performance and recovery outcomes.
What Types of Protein Supplements Are Available?
A diverse range of protein supplements exists, each with unique characteristics and applications. The most common types include whey protein, casein protein, and plant-based protein powders. Understanding the differences among these options can aid athletes in selecting the most suitable supplement for their requirements.
Whey protein, derived from milk, is popular for its rapid absorption rate, making it ideal for post-workout recovery. Casein protein, also sourced from milk, digests slowly, providing a sustained release of amino acids, which is advantageous for overnight recovery. Conversely, plant-based protein powders, such as pea, rice, and hemp protein, cater to those with dietary restrictions or preferences.
Key categories of protein supplements include:
- Whey protein: Rapidly absorbed, perfect for post-exercise recovery.
- Casein protein: Slow-digesting, excellent for nighttime muscle repair.
- Plant-based protein: Ideal for vegans, offering diverse amino acid profiles.
- Egg protein: A complete protein source suitable for various diets.
By understanding the various types of protein supplements, athletes can make informed decisions that align with their dietary preferences and performance goals. This knowledge enhances their capacity to effectively meet protein requirements.
How to Select the Right Protein Supplement?
Choosing the appropriate protein supplement involves several critical considerations. Athletes should evaluate factors such as digestibility, amino acid profile, and individual dietary preferences when selecting a protein product. Those with lactose intolerance might favour plant-based options or whey protein isolate, which contains less lactose.
Furthermore, athletes should seek out supplements that are third-party tested for quality and purity. This guarantees that the product contains what it claims and is free from harmful contaminants.
Key factors to consider when selecting a protein supplement include:
- Digestibility: Assess how easily the body can absorb and utilise the protein source.
- Amino acid profile: Choose a supplement that provides a complete amino acid profile for optimal muscle recovery.
- Flavor and texture: Take personal preferences into account to ensure consistent usage.
- Price and quality: Balance cost with quality, opting for reputable brands with transparent labelling.
By carefully considering these factors, athletes can select the right protein supplement to enhance their nutritional strategies. This choice ensures they achieve their fitness objectives while maintaining overall health.
Weighing the Benefits and Risks of Protein Supplementation
Protein supplements can greatly assist in muscle recovery and growth. However, athletes must also be mindful of the potential risks associated with excessive protein intake. While protein is crucial for muscle health, an overabundance can lead to adverse effects, such as kidney strain and nutrient imbalances.
Moderate supplementation is generally safe for most athletes, particularly when used to complement a balanced diet. Nonetheless, it is essential to monitor total protein intake from both food and supplements to prevent overconsumption.
Key benefits of protein supplementation include:
- Supports muscle recovery: Facilitates faster recovery following workouts.
- Convenience: Provides an easy way to meet protein needs while on the move.
- Diverse options: Offers a variety of flavours and formats to suit personal preferences.
- Enhanced performance: Can lead to improved training outcomes when used appropriately.
By remaining conscious of protein supplementation, athletes can enjoy the benefits while minimising potential risks. This approach enables them to leverage the advantages of protein effectively and safely.
Integrating Protein with Other Nutrients for Optimal Athletic Performance
Understanding the Synergistic Relationship Between Protein and Carbohydrates
Protein and carbohydrates work together synergistically to fuel workouts and enhance recovery. For athletes, balancing these macronutrients is vital for achieving optimal performance. While protein promotes muscle repair and growth, carbohydrates serve as the primary energy source during intense training and competition.
During exercise, muscles predominantly rely on carbohydrates for energy. However, following exercise, the combination of protein and carbohydrates is critical for maximising recovery. Consuming protein alongside carbohydrates can enhance glycogen replenishment, enabling athletes to restore energy levels more efficiently.
Key interactions between protein and carbohydrates include:
- Energy supply: Carbohydrates provide energy for workouts, while protein supports recovery.
- Glycogen replenishment: Combining both nutrients post-exercise optimises glycogen stores.
- Muscle recovery: Protein assists in repairing muscle tissue after carbohydrate-fuelled workouts.
- Improved performance: A balanced intake of both nutrients sustains athletic performance.
By understanding how protein interacts with carbohydrates, athletes can create superior nutrition strategies. This balance is essential for maximising energy levels and enhancing overall athletic performance.
The Vital Role of Fats in a Protein-Rich Diet
Fats are essential in a diet rich in protein, supporting hormone production and overall health. While protein is fundamental for muscle maintenance, fats provide essential fatty acids necessary for various bodily functions. Healthy fats promote hormone production, which is crucial for muscle growth and recovery while assisting in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Athletes should focus on incorporating healthy fat sources into their diets, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Balancing fat intake with protein ensures athletes receive comprehensive nutrition that supports both performance and recovery.
Key roles of fats in a protein-rich diet include:
- Hormone production: Healthy fats aid in synthesising hormones important for muscle growth.
- Energy source: Fats provide a concentrated energy source, particularly during low-intensity activities.
- Nutrient absorption: Fats facilitate the absorption of vitamins A, D, E, and K.
- Overall health: A balanced fat intake promotes heart health and cognitive function.
By recognising the significance of fats in a protein-rich diet, athletes can ensure comprehensive nutrition. This approach fosters optimal performance and overall health.
Strategies for Achieving a Balanced Diet for Peak Athletic Performance
Athletes must balance protein intake with other nutrients to maintain overall health and enhance performance. A well-rounded diet comprising carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals is essential for supporting the diverse needs of athletes. Each nutrient plays a unique role in performance, recovery, and overall well-being.
Incorporating a variety of foods from all food groups guarantees that athletes receive the necessary nutrients for optimal function. This balance not only improves performance but also helps prevent nutritional deficiencies that could impede athletic capabilities.
Key strategies for maintaining a balanced diet include:
- Diverse food choices: Include a wide range of foods to meet nutrient requirements.
- Meal planning: Organise meals to ensure balanced macronutrient distribution throughout the day.
- Hydration: Maintain adequate hydration to support overall health and performance.
- Regular monitoring: Track dietary intake to maintain balance and make adjustments as needed.
By focusing on a balanced diet, athletes can optimise their training and performance outcomes. This holistic approach enhances health, recovery, and overall athletic potential.
Frequently Asked Questions About Protein and Athletic Performance
What is the recommended daily protein intake for athletes to optimise performance?
Athletes should generally consume between 1.2 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, depending on their specific sport and training intensity.
Which protein sources are most effective for athletes?
High-quality protein sources include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and plant-based proteins like quinoa and tofu.
When is the best time to consume protein for maximum benefit?
The optimal time to consume protein is immediately after workouts, but it can also be beneficial before bedtime and throughout the day when spread across meals.
Can protein supplements assist in muscle recovery?
Yes, protein supplements can support muscle recovery, particularly when dietary intake is insufficient or for quick post-workout nutrition.
What potential risks are associated with excessive protein intake?
Excessive protein consumption may lead to health issues such as kidney strain, nutrient imbalances, and digestive discomfort.
Do endurance athletes require more protein than strength athletes?
Endurance athletes typically need less protein than strength athletes, focusing more on carbohydrates for energy while still needing adequate protein for recovery.
How does protein influence athletic performance outcomes?
Protein enhances athletic performance by supporting muscle repair, growth, and recovery, resulting in improved overall physical capabilities.
What types of protein supplements are available for athletes?
Common types of protein supplements include whey, casein, plant-based options, egg protein, and various protein blends, each offering unique benefits.
How can athletes ensure they are obtaining high-quality protein?
Athletes should focus on high-quality protein sources that provide a complete amino acid profile and are easily digestible, ideally sourced from reputable brands.
Is it necessary for all athletes to take protein supplements?
No, protein supplements are not essential for all athletes; they should be used strategically to fill dietary gaps when whole food protein intake is insufficient.
Connect with us on Facebook!
The Article How Athletes Use Protein Daily: A Universal Guide appeared first on https://athleticsupplement.com
The Article Protein Daily Use by Athletes: A Comprehensive Guide Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com